edible hydrophobic coating
Disclosed is an edible coating a food product coated with the coating and the. Our coatings display high contact angles and low roll.
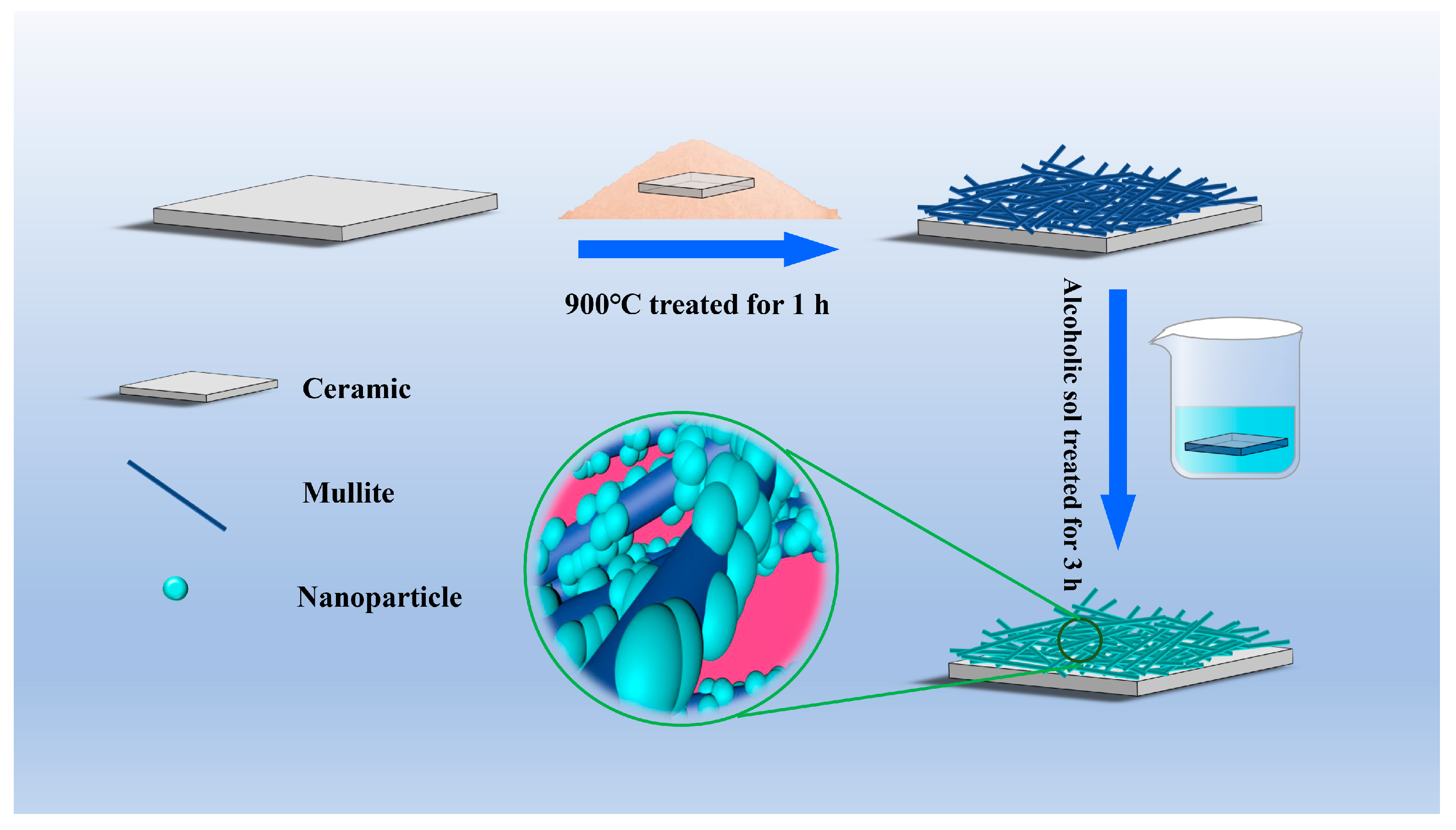
Coatings Free Full Text Robust Superhydrophobic Coating With Mullite Fiber Framework Html
Edible films and coatings may be defined as protective layers created around food surface by applying solutions made from edible polymers like polysaccharides proteins lipids or their combinations.
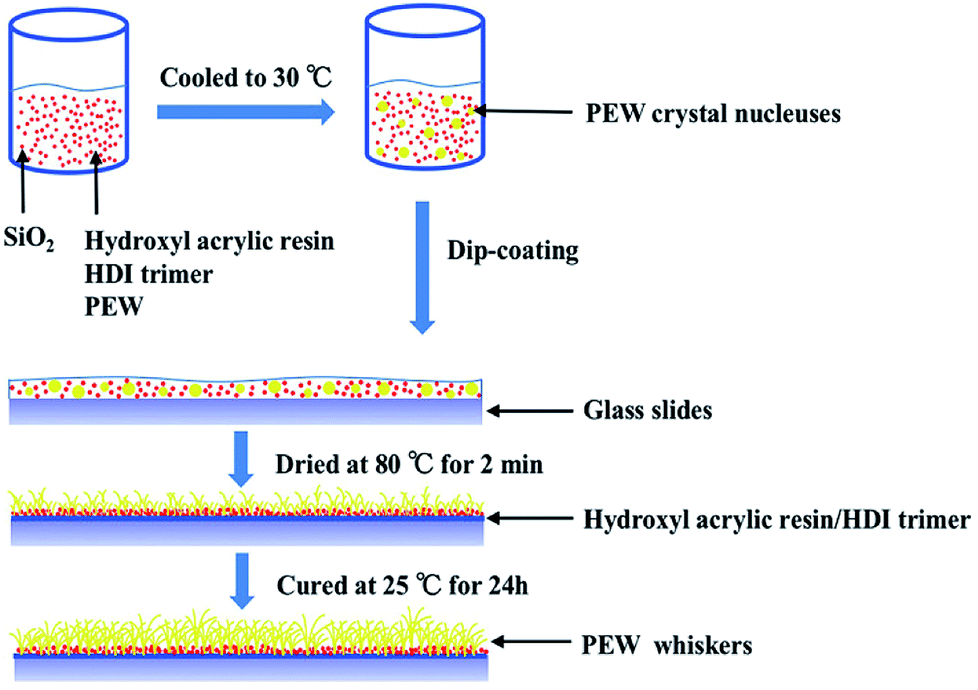
. HPMCOA coatings containing 2 wv sodium benzoate SB 1 ammonium carbonate AC 1 potassium carbonate PC 1. This coating surface has the similar micronanoscale structure to that of the leaf surface. The food product having the coating is resistant to becoming soggy.
Nevertheless their use can have more innovative uses beyond their current applications. Gestión en línea. The application of edible films and coatings is an easy way to improve the physical strength of the food products reduce particle clustering and enhance the visual and tactile features of food product surfaces Cuq et al 1995.
O 2 permeability at 14 1C and 55 5 RH ranged from 150 to 795 cm 3 cm cm 2 s 1 Pa 1 with CO 2 permeability 2 to 6 times as high. In addition these coatings can store latent heat. In contrast the edible coating forming solution is applied to the food product.
Professor Ilker Bayer from the Italian Institute of Technology in Genova Italy address these issues by forming hydrophobic and superhydrophobic smart coatings based on bees wax and water. The coated surface was dried at room temperature to realize the superhydrophobic properties. Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose HPMC and food preservatives were developed as edible coatings for antifungal ingredients.
In this work a thermo-resistant edible super-hydrophobic coating has been fabricated using beeswax and coffee which are approved by US. The coating matrix results in. 13 2018 Researchers have developed a super-thin non-toxic lightweight edible ultra-white coating that could be used to make brighter paints and coatings for use in the cosmetic food.
In another study Y. A variety of liquid foods can freely roll on this coating surface in spherical. Fruits and vegetables are coated in nature by a natural waxy coating called cuticle consisting of a layer of fatty acid-related substances such as waxes and resins with low permeability to water Baldwin 1994.
Composite edible coatings based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose HPMC as a polymeric phase and oleic acid OA or beeswax BW as a hydrophobic phase were formulated with different food additives as antifungal ingredients. Wax was the first coating used in fruits specifically in citrus fruits. It is free from waxes and has been designed with optimal hydrophilic-hydrophobic balance to achieve good water vapor resistance and barrier properties.
Prepared an edible superhydrophobic coating from beeswax and lignin extracted from coffee beans by dispersing them in a mixture of acetone and n-hexane Zhang et al 2019. Permeability to noncondensable gases O 2 and CO 2 was higher for hydrophobic peanut oil followed by beeswax coatings as compared to hydrophilic whey protein concentrate and carboxymethyl cellulose. Gelatin coatings usually depict good transparency mechanical and barrier properties and can be manufactured via an extrusion or casting process.
Edible films and coatings enhance the quality of food products by protecting them from natural deterioration processes. The coating exhibited superhydrophobicity for several food liquids such as milk tea cola and so on. Encouragingly the concept of fabricating nontoxic roll-off and superhydrophobic coatings with edible materials for readily slicking away residual fooddrink-related liquids was recently proposed and demonstrated by researchers from two universities in the United States Colorado State University and University of Illinois at Chicago Wang et al.
The significant difference is that in edible film solid edible laminate is wrapped around the food products. This edition of the Advanced Coating Surface Technology Opportunity Engine highlights innovations related to edible food coatings hydrophobic coatings wood coatings and self-healing coatings across several broad industries. The Advanced Coating Surface Technology Opportunity Engine provides intelligence on technologies products processes.
We used FDA-approved edible materials to fabricate superhydrophobic coatings in a simple low cost scalable single step process. This protective layer acts as a barrier between the food and external environment and thus delay the ripening and spoilage process. Research on edible superhydrophobic coatings for food packaging material 205 sprayed onto the surface of glass a distance of 50 cm with PP as a binder to improve its robustness.
Texcoat FV Pro is a proprietary triglyceride based edible coating. Gelatin is a hydrophobic protein usually found in wheat which is also a globular protein and also used in some edible coatingsfilms due to its low cost and availability. As the previously conducted experiment indicated that both the sprayed coatings of emulsion-prepared carnauba wax and beeswax particles could possess superhydrophobicity 33 41 when water droplet is dropped.
Edible films are made by casting and the extrusion process and coating of the edible solution are done by dipping and spraying. Edible coatings as a structural matrix An edible coating is a thin layer of material that can be consumed and provides a barrier to moisture oxygen and solute movement for the food Falguera et al. In other words the team has created an effective phase change material PCM from natural materials.
Fabrication of edible wax powder. The edible hydrophobic powder was prepared through two stage evaporations of wax-in-ethanol emulsion. Food and Drug Administration.
They were tested as coatings on clementine oranges and all the coatings effectively reduced the mass loss without adversely affecting the sensory flavor and appearance of the fruit Valencia-Chamorro et al.

Superhydrophobic Coatings With Beeswax And Carnauba Wax Youtube
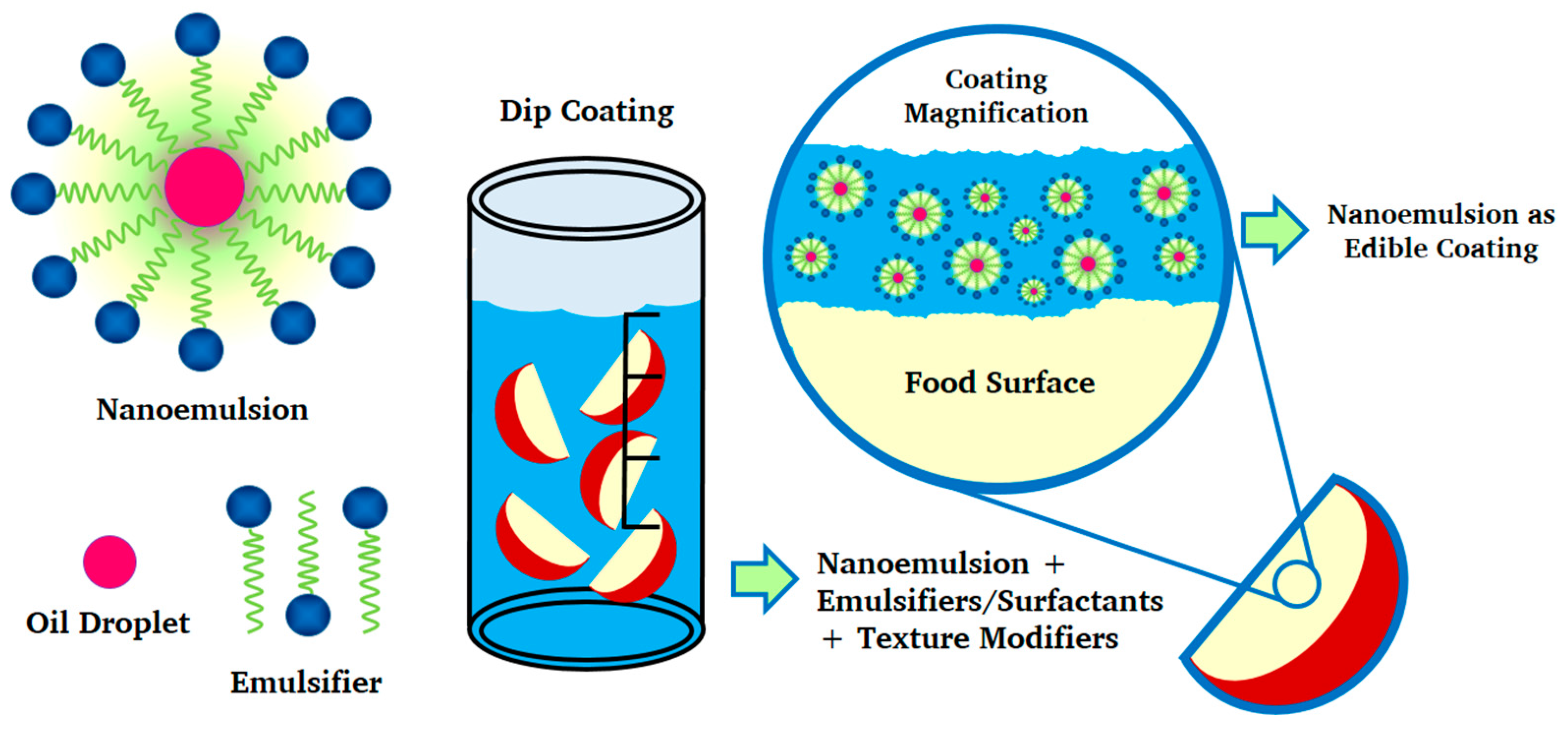
Ijms Free Full Text Nanosystems In Edible Coatings A Novel Strategy For Food Preservation Html

Superhydrophobic Coatings With Edible Materials Youtube

Edible Coating Can Empty Every Last Drop Of Sticky Liquids Like Ketchup Honey Or Syrup
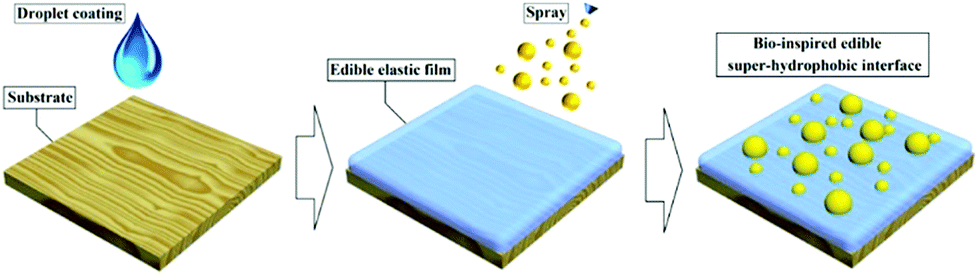
Bio Inspired Sustainable And Durable Superhydrophobic Materials From Nature To Market Journal Of Materials Chemistry A Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C9ta05185f
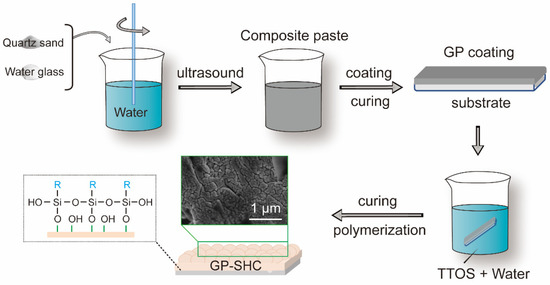
Coatings Free Full Text A Superhydrophobic Alkali Activated Materials Coating By Facile Preparation Html
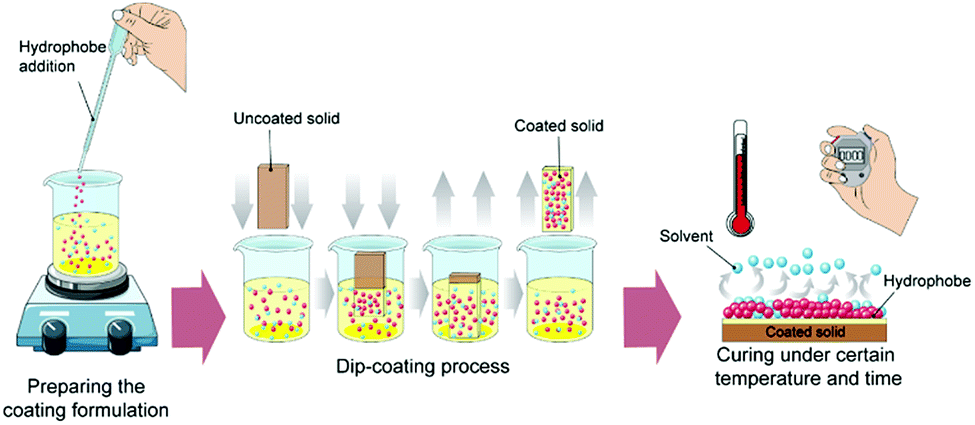
Bio Inspired Sustainable And Durable Superhydrophobic Materials From Nature To Market Journal Of Materials Chemistry A Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C9ta05185f

Schematic Representation Of Biodegradable And Edible Active Coating Download Scientific Diagram

Effect Of Various Additives On The Properties Of The Films And Coatings Derived From Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose A Review Ghadermazi 2019 Food Science Nutrition Wiley Online Library

Functional Food Packaging For Reducing Residual Liquid Food Thermo Resistant Edible Super Hydrophobic Coating From Coffee And Beeswax Sciencedirect
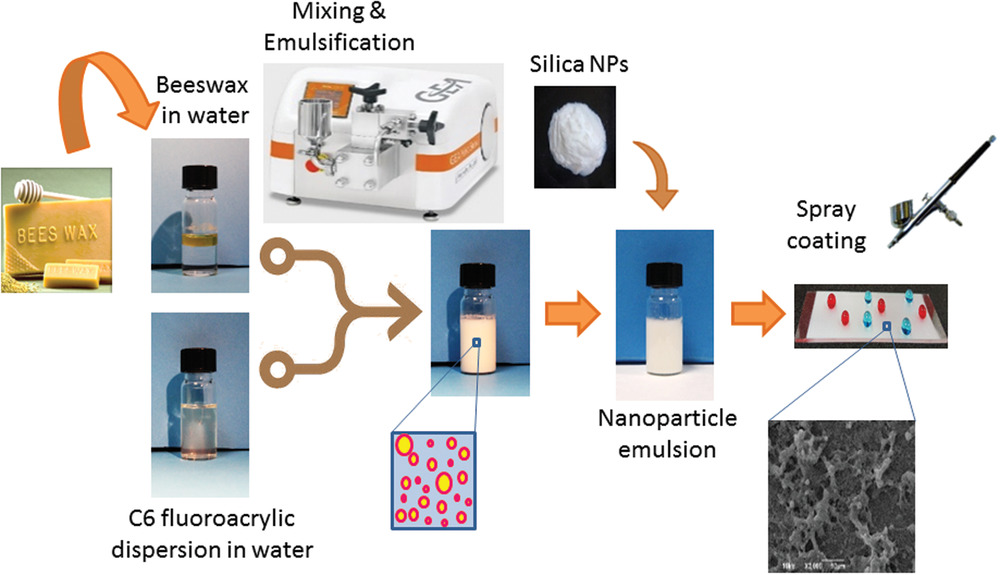
Superhydrophobic Coatings From Beeswax Advanced Science News

Edible Coating An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Edible Films Coatings Usage To Prolong Food Stability Technology Times

Design And Fabrication Of Vapor Induced Superhydrophobic Surfaces Obtained From Polyethylene Wax And Silica Nanoparticles In Hierarchical Structures Rsc Advances Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C8ra01666f

Fabrication Of Superhydrophobic Coatings With Edible Materials For S

Schematic Representation Of Production Of Films And Coatings Download Scientific Diagram
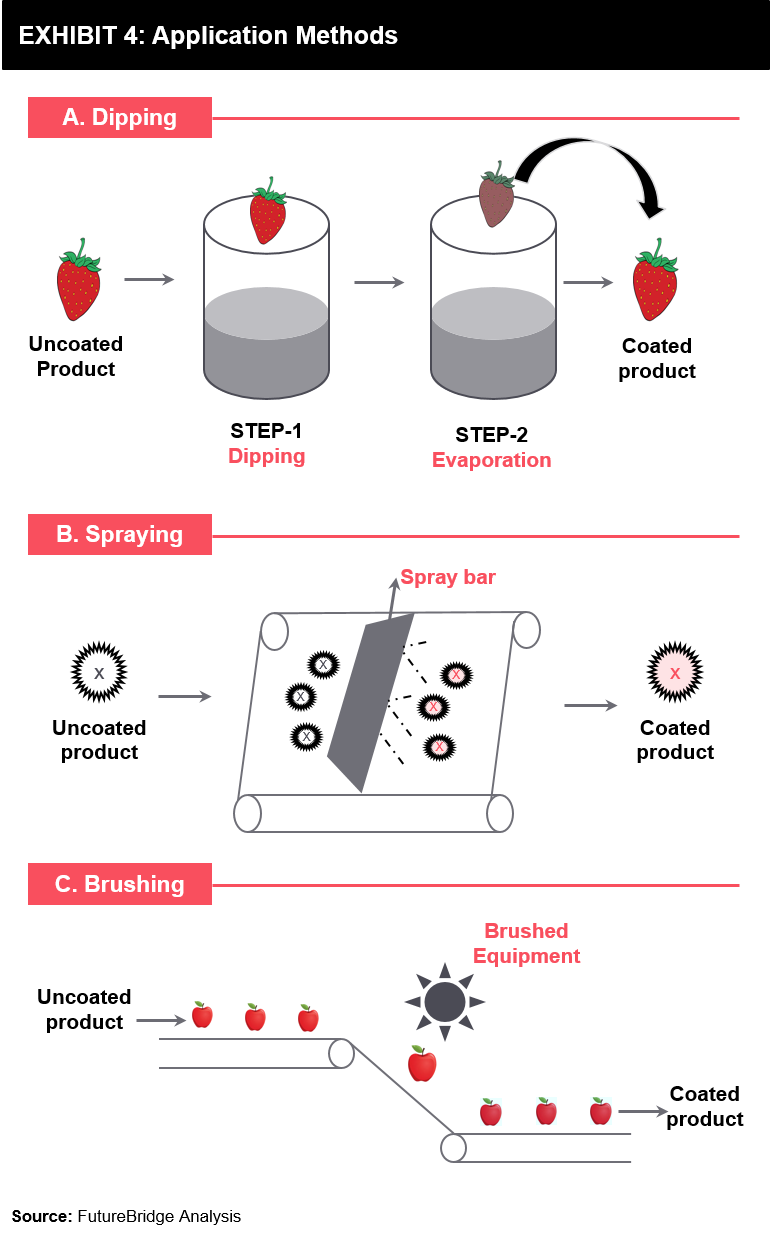

0 Response to "edible hydrophobic coating"
Post a Comment